Customer Service Transformation, Large Language Model, Voice
How Voice AI in the Age of Generative AI and LLMs is Reshaping Banking
With the power of Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs), voice has re-emerged as a critical channel for customer interactions—smarter, more automated, and more personalized than ever before.
No longer a challenging channel to automate, thanks to advancements in Generative AI, LLMs, voice-to-text technology, and speech recognition, Voice AI Bots and Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVAs) can now engage in fluent, context-aware conversations that feel natural and intuitive. This transformation is especially impactful in interaction-intensive industries like banking, where customer interactions often involve complex, high-value tasks.
What challenges have now been overcome in automating the voice channel?
How have advancements in AI and other technologies fueled the importance of Voice?
This blog sets out to answer these key questions and to highlight why voice is a critical channel for banks.
Before: The Challenges with Voice AI prior to Advancements in Generative AI and LLMs
Historically, voice has been an attractive channel for customers to interact with their banking providers. Although it was a costly channel for service providers to support, the fact remains that many banking customers prefer to engage via voice calls. For them, making a verbal request is often faster and easier than typing out a message in an app or email.
However, earlier Voice AI technologies and systems were challenging to automate due to limitations in several key technologies. The technology made natural, accurate, and flexible voice interactions difficult to achieve, such as:
- Speech Recognition Struggles: Early speech-to-text systems had difficulty accurately transcribing spoken language, especially with accents, background noise, varied speech patterns, or fast-paced conversation. For example, a customer asking, “Hey, what’s my balance after the last two payments?” could easily be mis-transcribed, leading to incorrect responses or failure to understand the query.
- Rigid Intent Recognition: Traditional Voice AI relied on rule-based intent matching, which required users to speak in very specific ways to be understood. If a Voice Bot was trained to recognize “Check balance,” it might fail to understand variations like “How much money do I have?” or “Can you tell me my current balance?” This lack of flexibility often frustrated users and made interactions feel unnatural.
- Lack of Context and Personalization: Legacy systems couldn’t hold context over multiple turns in a conversation. If a user asked, “What’s my balance?” followed by, “Can you transfer $100 to my savings?” the system often couldn’t link the two or remember the context. This made multi-turn conversations and personalized service nearly impossible.
- Structured Dialogue Only: Voice bots needed users to follow rigid, structured flows, often requiring exact information in a fixed order—like first giving an account number, then specifying the transaction type, and only then stating the amount. Deviating from this sequence would cause the system to fail or transfer the call to a human agent.
- Verification Challenges: Verifying user identity via voice was complex and error-prone. Without advanced biometric authentication, users had to answer security questions or enter PINs, adding friction and making automation less appealing.
These limitations made Voice AI clunky, frustrating, and costly to maintain, leading many organizations to avoid fully automating the voice channel and focus on messaging and text-based channels where higher degrees of automation were possible.
Advancements in AI and speech technologies have, however, transformed this landscape, enabling more accurate speech recognition, nuanced understanding, contextual memory, and natural conversation flow—making voice a viable, even preferred, channel for automation today.
Now: The Possibilities of Voice AI Bots, powered by Generative AI and LLMs
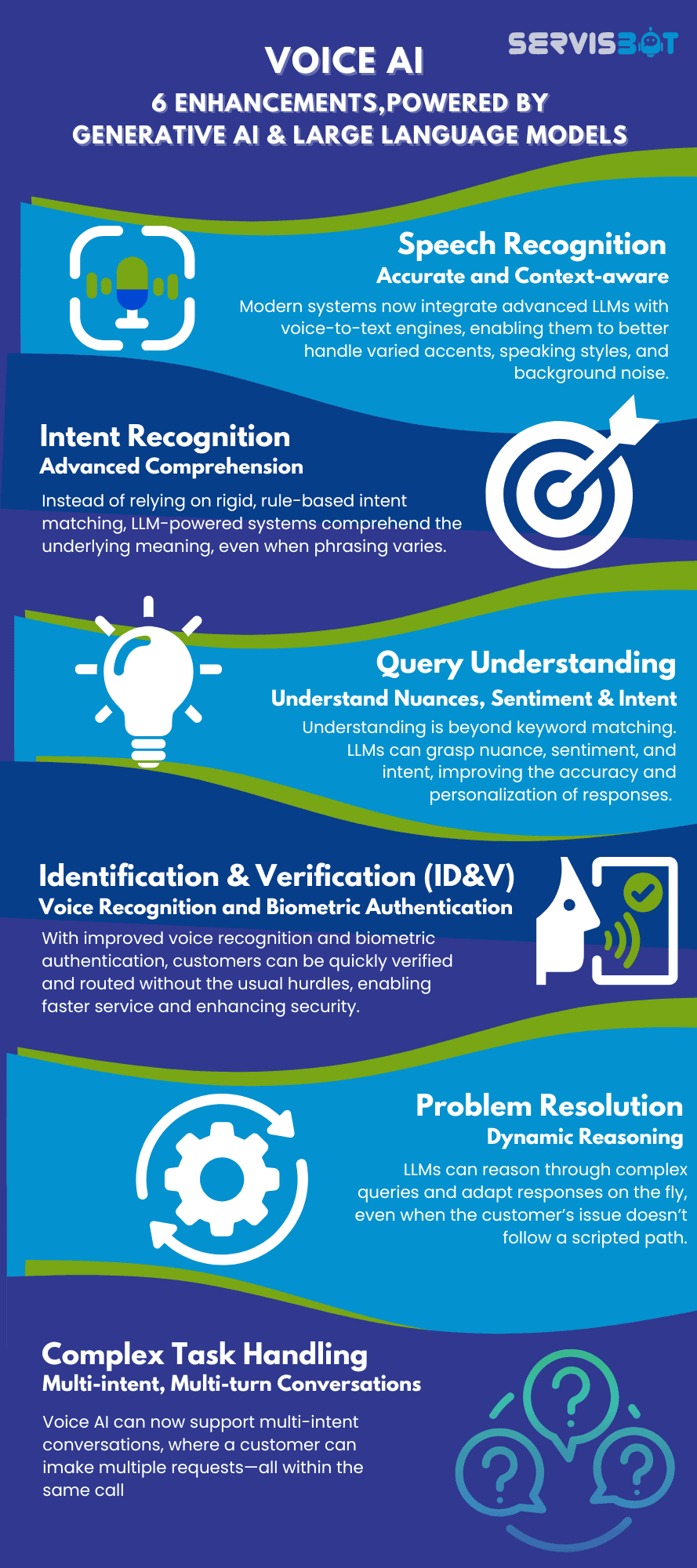
Advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI have fundamentally transformed the capabilities of Voice AI, directly addressing the limitations of earlier AI and speech technologies. Here are 6 ways in which they have reshaped the power of Voice AI:
- Speech Recognition is More Accurate and Context-aware. Modern systems now integrate advanced LLMs with voice-to-text engines, enabling them to better handle varied accents, speaking styles, and background noise. This means a customer can ask, “Can you tell me how much I spent last week?” and the AI can accurately transcribe and interpret the query, even if phrased in a non-standard way.
- Better Intent Recognition & Understanding. LLMs allow voice bots to understand a much broader range of natural language expressions without requiring exact matches. Instead of relying on rigid, rule-based intent matching, LLM-powered systems comprehend the underlying meaning, even when phrasing varies. For instance, a banking customer might say, “Did my paycheck come in?” or “Has my salary been deposited?”—both of which can now be understood as a request to check incoming transactions.
- Dynamic Conversation Flow. Conversation flow is no longer a fixed, slot-filling process. LLMs support flexible, dynamic dialogue, allowing users to interact naturally, switch topics, ask follow-up questions, or provide information out of sequence. These models can retain context across multiple turns, enabling more human-like interactions. For example, after confirming a balance, the AI can seamlessly respond to, “Great, can I transfer $200 to my savings?” without needing the customer to re-state their account details.
- Query Understanding has also evolved beyond keyword matching. LLMs can grasp nuance, sentiment, and intent, improving the accuracy and personalization of responses. In addition, biometric voice authentication and AI-driven fraud detection have reduced friction in customer verification, enabling secure and efficient voice interactions without cumbersome authentication steps.
- Identification & Verification (ID&V). With improved voice recognition and biometric authentication, customers can be quickly verified and routed without the usual hurdles, enabling faster service and enhancing security
Beyond addressing past limitations, Generative AI and LLMs are opening new possibilities for Voice AI in banking, such as:
- Proactive Assistance: Voice AI can suggest actions based on past behavior, like prompting a customer to schedule recurring payments.
- Emotional Intelligence: Sentiment analysis helps detect frustration or urgency, allowing the system to escalate to a human agent when needed.
- Complex Task Handling: Voice AI can now support multi-intent conversations, where a customer can inquire about balances, request a card replacement, and initiate a fund transfer—all within the same call. For instance, a simple question like “What’s my balance?” can prompt the AI to not only provide a real-time answer but also offer follow-up actions like transferring funds.
With a Voice AI Bot accurately interpreting speech, understanding sentiment, and responding appropriately, the friction is greatly reduced, automation is increased, and customer experience is enhanced.These advancements are making voice a powerful, personalized, and efficient channel for banking, transforming customer service into a more seamless, personalized and intelligent experience.
The Benefits of Voice AI Bots for Banking
Unlike a few years ago, Voice AI is now capable of handling routine banking tasks all through natural, conversational and voice interfaces. It is no wonder that Voice AI Bots are being embraced by customer service and support teams as they reap the multiple benefits of:
Improved Customer Experience:
Fast, natural, and frictionless interactions on the often preferred voice channel, allow customers to resolve issues or get information without navigating complex menus, typing lengthy queries, or waiting on hold.
24/7 Availability:
Voice bots operate around the clock, enabling banks to provide consistent support and service at any time, enhancing accessibility for customers.
Cost Efficiency:
Automating routine voice interactions reduces the need for human agents, lowering operational costs and enabling human agents to focus on high value or critical customer issues.
Faster Resolution & Shorter Call Times:
Voice bots can quickly authenticate users, understand queries, and provide instant responses, improving efficiency and reducing average handling time.
Scalability:
Banks can handle large volumes of customer calls simultaneously, especially during peak times, without compromising service quality.
Enhanced Security:
Voice biometrics and AI-driven verification reduce fraud risk while streamlining identity authentication processes.
As Voice AI continues to evolve, it’s clear that voice is no longer just a legacy channel; it’s a powerful, frictionless medium for personalized and efficient customer experiences, powered by the intelligence of LLMs and Generative AI.
To learn more about how generative AI can transform your customer service efficiency in ways that are safe and effective, contact us for more information and a demo.
In the meantime check out our AI resources.