AI, Large Language Model
The Role of AI Assistants, AI Agents and AI Copilots, powered by Generative AI
A range of AI Assistants, powered by Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs), are being deployed at rapid rates by businesses to reshape core functions and workflows, from customer service to other operational areas. They are proving to deliver unprecedented levels of automation, personalization, and efficiencies that are impossible to ignore. They are thereby unlocking new opportunities and transforming business as usual.
Generative AI Assistants versus NLP-based Chatbots
What is so special about these Gen AI Assistants compared with past chatbot solutions, that were powered by natural language processing (NLP) technology?
Generative AI assistants stand out from their precursor chatbot solutions, primarily due to their ability to generate human-like, contextually relevant responses in real time. While traditional chatbot solutions powered by natural language processing (NLP) were often rule-based and relied on pre-programmed scripts, generative AI models are built on advanced machine learning architectures like large language models (LLMs). These models are trained on vast amounts of data, enabling them to understand context, nuances, and even implicit meanings in user input. As a result, generative AI assistants can craft highly dynamic, more personalized, and adaptive responses, making interactions feel more natural and engaging.
Generative AI assistants especially excel at handling complex, multi-turn conversations and providing creative, personalized solutions. Unlike earlier chatbots that struggled with ambiguity or required strict keyword matching to function effectively, generative AI can infer intent from incomplete or imprecise input. This flexibility allows them to assist with a wider range of tasks, from answering intricate questions to generating creative content or solving unique problems. Additionally, generative AI can learn and adapt over time, enhancing its ability to serve users in diverse contexts, which makes it a revolutionary step beyond the more static and limited capabilities of traditional NLP-powered chatbots.
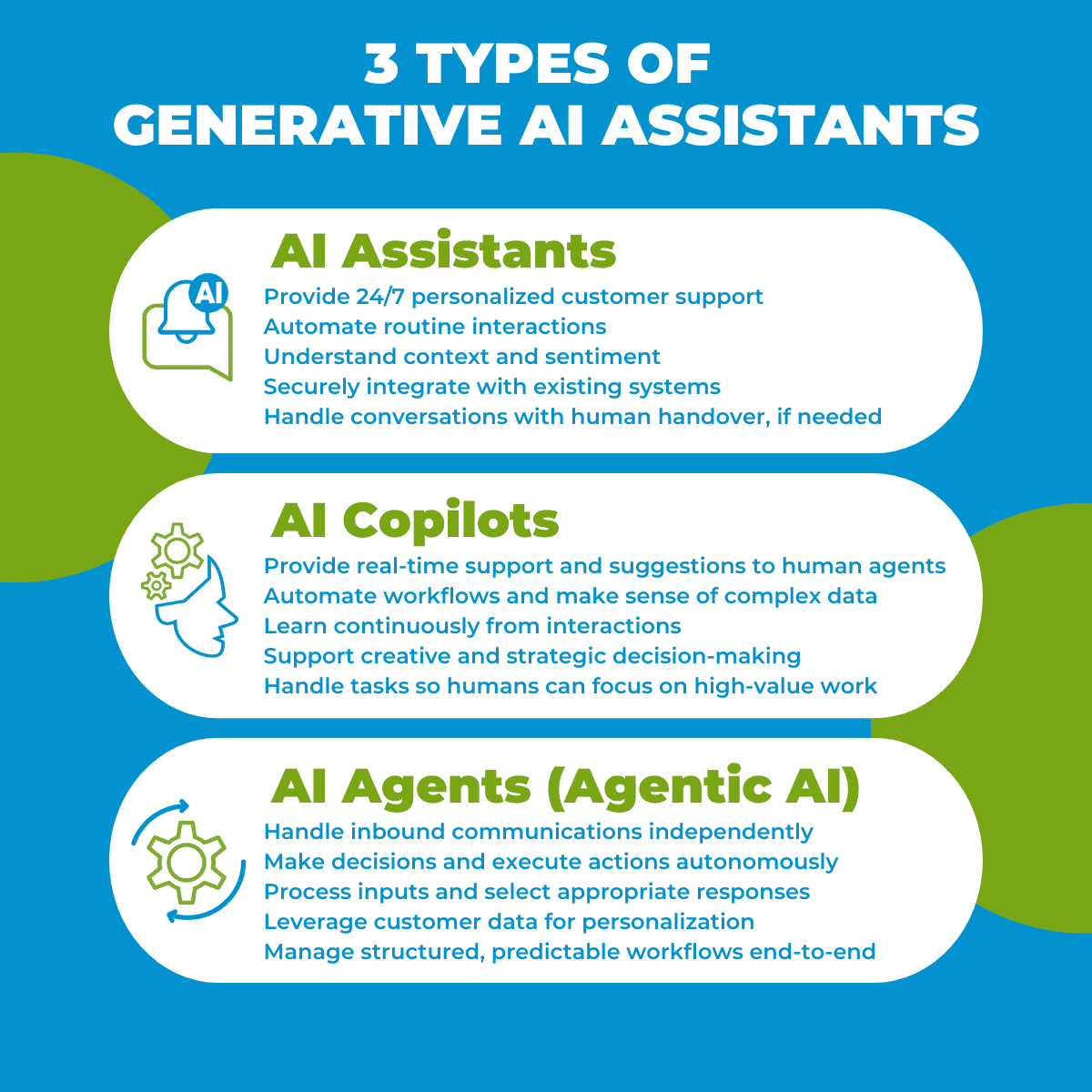
Three Categories of AI Assistants and their Roles in Customer Service
Not all AI assistants in the realm of generative AI are the same, however. The technology can be applied to create different types of digital workers that can be applied to varying use cases across a business. At ServisBOT, we classify these in three categories: AI Assistants, Autonomous AI Agents, and AI Copilots.
For the sake of this blog, let’s take a look at customer service since it is a function that has widely embraced Generative AI. A recent global survey, conducted by the IBM Institute for Business Value (IBM IBV), polled 1,500 customer service managers among organizations that had already adopted traditional conversational AI in their customer service function. Their findings were:
“Every leader we surveyed says their organization plans to use generative AI in customer service—and 67% say they’ve already begun.”
1. AI Assistants
AI Assistants designed for customer service are powered by generative AI and conversational AI. They enhance customer engagement and automate interactions across various channels, including voice, text, email, and web. They help provide a seamless, personalized customer experience, automating routine interactions and handing off to an agent or human-in-the-loop when needed. This allows for higher levels of self-service and takes the burden of responding to routine queries away from human agents who can then focus on more complex customer issues.
They can respond on voice channels with human-like speech using text-to-speech (TTS) technology or on messaging and email channels. Their ability to understand context and sentiment and to generate content and replies enables them to hold contextually-aware conversations with customers, often resolving issues with little human intervention.
AI Assistants can integrate securely with existing business systems, such as CRM platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot, allowing them to pull in customer records and data that allows them to provide more sophisticated and personalized service. They can equally update customer records with new insights from interactions, making these available to human agents.
For businesses, these AI assistants improve operational efficiency and reduce operational costs by reducing the workload on human agents and enhancing first-contact resolution rates. Customers benefit from instant, 24/7 support with a consistent, high-quality experience tailored to their needs. By combining generative AI’s flexibility with conversational AI’s interaction capabilities, this assistant becomes a valuable tool for modern customer service strategies.
2. AI Copilots
AI Copilots powered by large language models (LLMs) are intelligent assistant systems that work alongside human employees to enhance productivity and decision-making across various business functions. These systems leverage advanced natural language processing capabilities to understand context, generate responses, and perform complex tasks that traditionally required human expertise.
In banking, AI copilots are transforming operations in several key areas. Customer service representatives use them to instantly access account information, regulatory guidelines, and product details during client interactions, enabling faster and more accurate responses. Risk analysts employ copilots to summarize complex financial documents, identify potential compliance issues, and generate preliminary risk assessments. Loan officers leverage these systems to streamline application processing by automatically extracting relevant information from documents and cross-referencing credit histories.
Investment advisors use AI copilots to quickly analyze market trends, generate portfolio recommendations, and create personalized investment summaries for clients. Back-office operations benefit from automated report generation, regulatory filing assistance, and fraud detection support.
The key advantage is that these copilots don’t replace human judgment but augment it, handling routine information processing while humans focus on relationship building, strategic thinking, and complex decision-making. Banks report significant improvements in efficiency, consistency, and employee satisfaction when implementing AI copilot systems across their operations.
In essence, AI copilots are great where complexity and nuance demand a human in the loop. They don’t take over the entire show; they just make things run smoother and faster. This distinction matters a lot for organizations wary of fully automated solutions or newly-embraced AI technologies.
3. AI Agents (Agentic AI)
AI Agents are highly advanced autonomous systems designed to handle inbound voice calls, emails, texts, or in-app messages in a customer service role. These self-sufficient AI systems are sometimes referred to as Agentic AI. They are designed to perform tasks with a degree of autonomy, acting as “agents” capable of making decisions, executing actions, and achieving goals without constant human intervention. These systems are equipped with capabilities that allow them to process inputs and make informed choices to interact effectively with customers.
Unlike traditional support systems that rely on predefined scripts or human oversight, these agents use the combined capabilities of large language models (LLMs) and conversational AI to understand, respond to, and resolve customer queries.
A Voice-based AI Agent, for example, is powered by advanced speech recognition and natural language understanding and can interact fluidly with customers, providing quick info or guiding them through a step-by-step process. A caller might ask, “What’s the status of my order?” and the phone agent would pull up the relevant data, confirm the user’s identity, and share an expected delivery date, all without a human picking up a handset.
Though they’re not human, these agents can leverage historical customer data and be integrated with backend business systems to personalize the experience. For example, a returning caller might have a history of certain inquiries—maybe they frequently ask about warranty details. The agent can remember this pattern and proactively address it next time the customer calls, easing friction and making the experience feel very personal.
Of course, these agents are no substitute for human empathy. They can be trained to convey a friendly tone, but certain complex situations—maybe an upset customer with a nuanced complaint—still benefit from a human voice stepping in.
How AI Agents Differ from AI Assistants and AI Copilots
Autonomy vs. Collaboration: AI Agents tend to work solo. They thrive on structured tasks, handling calls end-to-end without any human nudges. Meanwhile, AI Assistants and AI Copilots are more collaborative, providing assistance to human agents, rather than controlling the entire process themselves.
Routine vs. Complexity: AI Agents excel at repetitive, predictable workflows, like processing returns or confirming appointments. AI Copilots, however, are more effective at providing complex and timely support that an agent may need when dealing with a customer. AI Assistants can handle routine interactions solo but have a path to handing over to a human agent when they are no longer able to handle a query or issue. In many cases as businesses deploy their initial AI solutions the AI Assistant is a preferable path for them to take to gain confidence in the AI system.
Cost and Focus: While AI Agents can reduce staffing needs and bring down overhead costs, AI Copilots and AI Assistants often help teams focus on more complex or strategic efforts. By handling grunt work, like summarizing lengthy documents or suggesting improved communication phrases, AI Copilots let human agents invest energy in higher level tasks. Similarly, AI Assistants handle routine queries and customer interactions, allowing human agents to focus on complicated customer issues. All three types of assistants, however, have significant impact on costs through their increased impact on automation and efficiency.
Conclusion
Generative AI Assistants are playing increasingly important roles, especially in business areas like customer service. Their roles can vary so it can be helpful to consider them under three broad categories of AI Assistants, Autonomous AI Agents, and AI Copilots, with each serving unique purposes.
AI Assistants handle routine tasks across multiple channels, enhancing customer engagement and efficiency. Autonomous AI Agents operate independently, leveraging advanced AI to resolve queries. Meanwhile, AI Copilots work alongside human agents, providing real-time support and automating workflows to enhance decision-making. Together, these roles blend automation, personalization, and human collaboration, offering tailored, scalable, and efficient customer service solutions that boost efficiencies and improve customer and agent satisfaction.
To learn more about how generative AI can transform your customer service efficiency in ways that are safe and effective, contact us for more information and a demo.
In the meantime check out our AI resources.